Source Code can be found here: https://github.com/ASU-ASCEND/Spring-2025/tree/main/GroundStation/Groundstation
Ground Station Data Flow
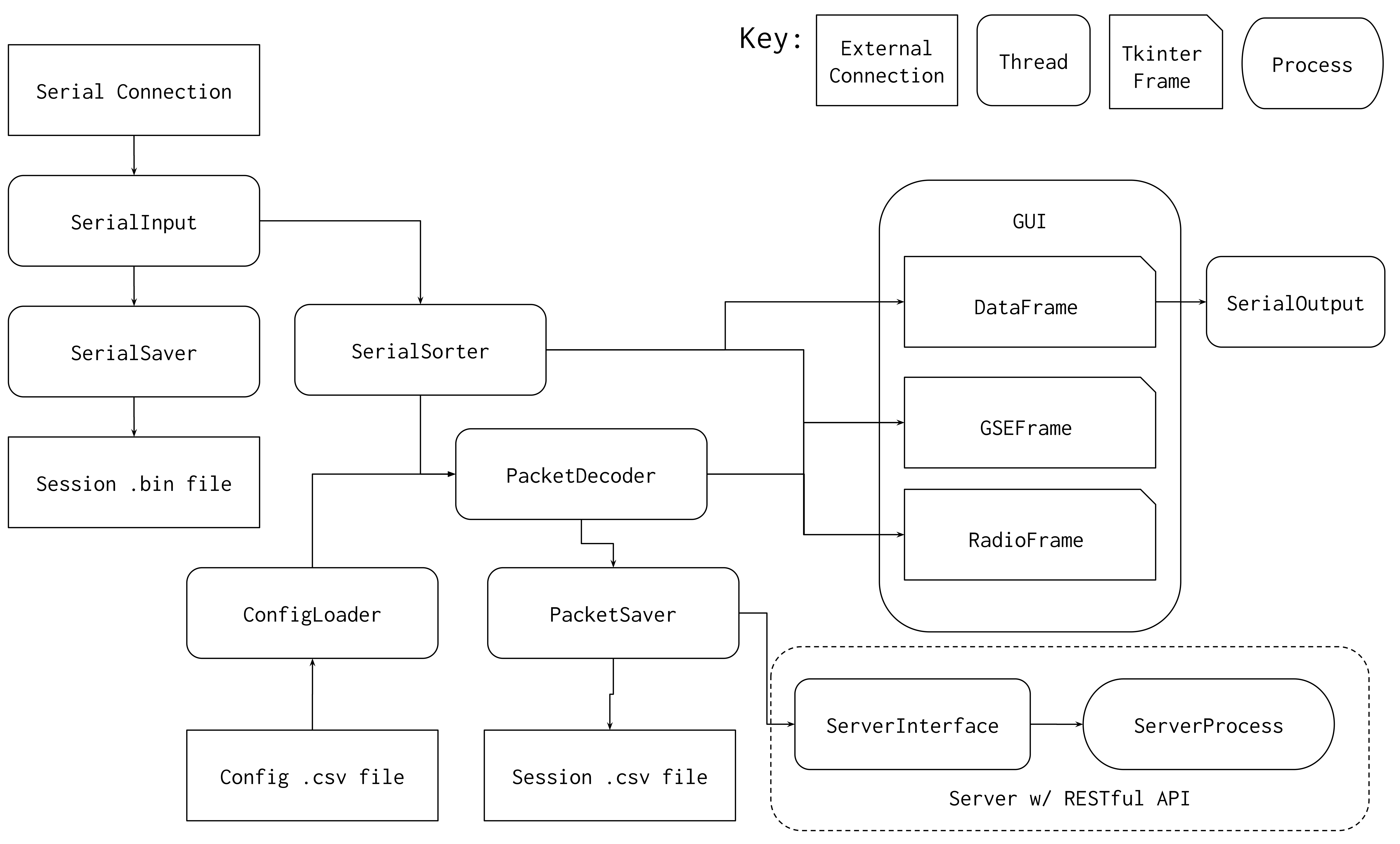
Some Notes on Using the Ground Station
(This information is also available here)
Before doing these steps make sure you have the most recent ground station software by running git pull somewhere in your local repo for the project (for example the folder that this README is in). All of the commands given in these instructions should be executed from the the folder /GroundStation/GroundStation.
Starting it up
The first time you run the ground station on a computer you need to either set up the .venv (see Development: Using venv) or install the dependencies onto your machine directly. Using venv is preferred, and you'll need to do Step 2 each time you start a new terminal.
After venv is set up you should see a (.venv) somewhere in the prompt the terminal you are using to indicate that the virtual environment is active.
Then to run the ground station software use:
If you get errors saying a package can't be found try activating the environment again even if it does say (.venv) in your terminal prompt, sometimes the (.venv) is leftover and isn't actually activated.
After running
You should see prompt in the terminal for which port to connect to, enter the index of the port for the usb device in the list. And the a prompt for which device to connect to, this is because the radio and pico serial connections use different baud rates so select the device accordingly.
Once in the gui, use the buttons on the top row to switch between operation modes. GSE and Radio are very similar and they should both save what they get to a file in the untracked folder session_data. The difference between the 2 is that Radio will give you packet dropping stats and GSE will give you Core debug messages. The last mode, Data, will let you get flash data off the payload and decode it, and the data we get from the SD Card, which will be saved as a binary as well.
Closing the ground station
To close the ground station, avoid using CTRL+C in the terminal as this has the danger of orphaning processes. Just close out of the GUI and then if a prompt is still open in the terminal you should be able to just press enter and it'll end the terminal portion of the program as well.
If you do use CRTL+C or the software crashes
If the software ends in an unexpected way or is interrupted it might be ok, but it does run the risk of not properly ending all of the processes associated with it. After that happens if you try to start it up again and see a bunch of new errors, they should be able to be fixed by the following:
- Make sure the current run is ended/closed using CRTL+C and force quits
- Open Task Manager and then search for and end every Python process (there may be some that aren't part of the ground station, especially if you are using VSCode, so if a process immediately reopens it should be fine to leave)
- Rerun the software (you may need to restart your venv)
Interacting with the RESTful API
The RESTful API has a single endpoint which can be interacted with via GET and POST. The server is intended to be hosted locally with the url for the single endpoint being: http://127.0.0.1:5000/dataserver
Adding Data
The server holds a single dictionary of values with keys set by the field name when it was posted. When the server receives a POST method with a duplicate key the new value replaces the old one. The POST method with then return the count of fields update in json format.
POST Example Using <tt>curl</tt>
Results in
Requesting Data
When requesting data the GET method takes a list of fields separated by commas and returns those fields corresponding value, if they exist in the dictionary, along with a boolean field called "missing_fields" which is true if at least one fields was not found, in json format.
GET Example Using <tt>curl</tt>
Results in
(Both examples can be called together using the script testDataServer.sh)
Development: Using venv
Use the provided requirements.txt file to automatically install needed dependencies
1\. Create a new local virtual environment
2\. Activate the new environment
Windows:
In Powershell:
In Git Bash:
Other OS:
3\. Install the requirements.txt
When done using the ground station software
Exit the virtual environment with: